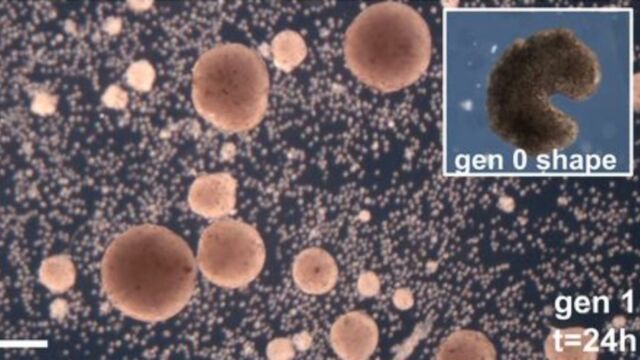
In 2020, researchers from the University of Vermont and Tufts University announced that they successfully managed to design and produce tiny programmable robots that were alive. They called them Xenobots, after the African frog Xenopus laevis.
Discover our latest podcast
By using adapted stem cells from the embryos of these very frogs, scientists were able to develop 1mm organisms that were not completely robots or animals. In one year, scientists discovered that these robots could walk, swim, regenerate themselves, and retain memories.
Most recently, a new study found that the Xenobots could also produce offspring—a massive breakthrough in modern technology. Joshua Bongard, study author and robotics expert at the University of Vermont says:
We found Xenobots that walk. We found Xenobots that swim. And now, in this study, we've found Xenobots that kinematically replicate.
Reproducing robots
Initially, the team noticed that the synthetic frog-bots were dying shortly after reproduction. So, in order to make it a more sustainable process, they used a supercomputer to modify the bots further. Lead author Dr. Sam Kriegman explains:
It's very non-intuitive. It looks very simple, but it's not something a human engineer would come up with. Why one tiny mouth? Why not five? We sent the results to Doug and he built these Pac-Man-shaped parent Xenobots.
Then those parents built children, who built grandchildren, who built great-grandchildren, who built great-great-grandchildren.
Greater purpose
Scientists believe that these Xenobots will be a useful solution for many contemporary issues. They can be used for intelligent drug delivery and also to clean up microplastics. Micheal Levin of Tufts University adds:
If we knew how to tell collections of cells to do what we wanted them to do, ultimately, that's regenerative medicine – that's the solution to traumatic injury, birth defects, cancer, and aging.
All of these different problems are here because we don't know how to predict and control what groups of cells are going to build. Xenobots are a new platform for teaching us.